Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Instrumentation Science and Opto-electronic Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 School of Physics, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
3 School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Glasgow, Glasgow G128QQ, UK
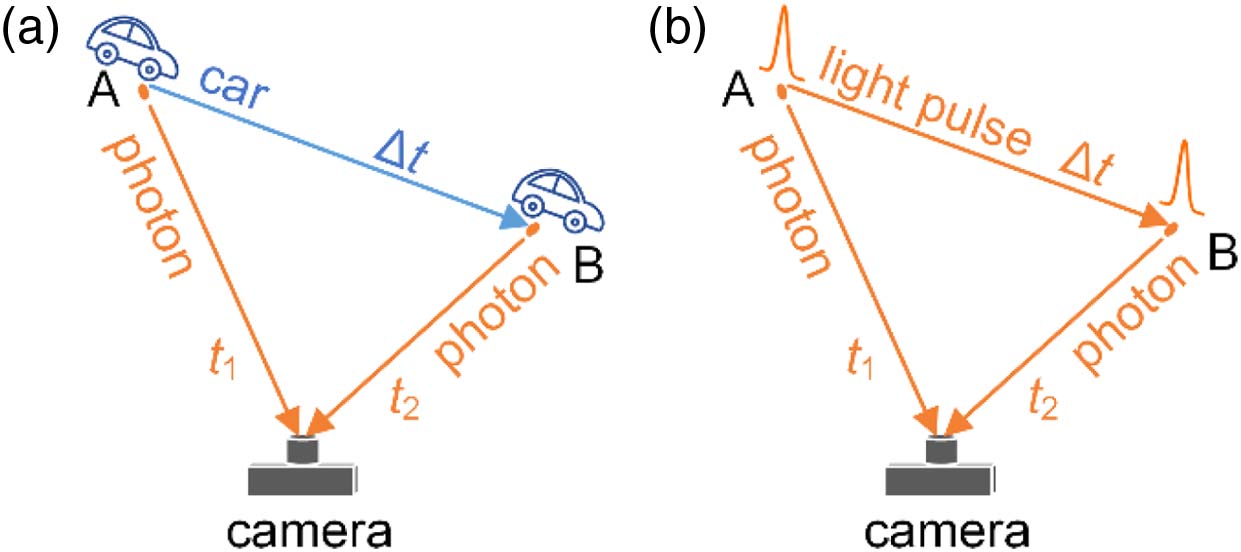
Light-in-flight imaging enables the visualization and characterization of light propagation, which provides essential information for the study of the fundamental phenomena of light. A camera images an object by sensing the light emitted or reflected from it, and interestingly, when a light pulse itself is to be imaged, the relativistic effects, caused by the fact that the distance a pulse travels between consecutive frames is of the same scale as the distance that scattered photons travel from the pulse to the camera, must be accounted for to acquire accurate space–time information of the light pulse. Here, we propose a computational light-in-flight imaging scheme that records the projection of light-in-flight on a transverse x?y plane using a single-photon avalanche diode camera, calculates and information of light-in-flight via an optical model, and therefore reconstructs its accurate (, , , ) four-dimensional information. The proposed scheme compensates the temporal distortion in the recorded arrival time to retrieve the accurate time of a light pulse, with respect to its corresponding spatial location, without performing any extra measurements. Experimental light-in-flight imaging in a three-dimensional space of is performed, showing that the position error is 1.75 mm, and the time error is 3.84 ps despite the fact that the camera time resolution is 55 ps, demonstrating the feasibility of the proposed scheme. This work provides a method to expand the recording and measuring of repeatable transient events with extremely weak scattering to four dimensions and can be applied to the observation of optical phenomena with ps temporal resolution.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(7): 07001072
1 中国海洋大学化学化工学院, 山东 青岛266100
2 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 山东 青岛266061
建立了毛细管电泳(CE)与电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)联用技术分析检测砷胆碱(AsC)、 砷甜菜碱(AsB)、 As(Ⅲ)、 二甲基砷酸(DMA)、 甲基砷酸(MMA)和 As(Ⅴ)六种形态砷化合物的方法。 结果表明, 六种砷化合物在20 min内即可得到有效分离, 各砷形态在2.0~50.0 μg·L-1范围内线性关系良好, 相关系数R2大于0.996, 检出限为0.10~1.08 μg·L-1, 5次平行测定中, 六种砷化合物峰面积的相对标准偏差(RSD)为3.0%~7.0%。 利用该方法成功对市售蓝点马鲛中砷化合物进行了测定, 加标回收率为93%~98%, 发现蓝点马鲛中的砷主要以AsB形式存在。 该方法具有稳定性好、 样品消耗量少、 快速、 简便等优点, 适用于其他生物样品中不同砷化合物的分析。
毛细管电泳 电感耦合等离子体质谱 形态分析 砷化合物 蓝点马鲛 Capillary electrophoresis (CE) Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry(ICP-M Speciation analysis Arsenic compound Scomberomorus niphonius 光谱学与光谱分析
2014, 34(6): 1675
1 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 山东 青岛 266061
2 青岛科技大学化学与分子工程学院, 山东 青岛 266042
3 中国海洋大学化学化工学院, 山东 青岛 266100
以HNO3-H2O2-HF为消解体系, 采用微波法对沉积物样品进行消解处理, 利用电感耦合等离子质谱法测定了普里兹湾(Prydz Bay)沉积物中Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm等16种稀土元素(rare earth elements, REEs)的含量, 并进行了配分模式分析。 从普里兹湾沉积物样品的分析数据和球粒陨石标准化配分模式可以看出: 稀土总量(∑REEs)变化范围为117.35~348.63 μg·g-1, 其中Ce含量较高, 在总量中占了很大比例; 各站位平均值为196.75 μg·g-1, 总量最大值是最小值的2.97倍; 各个站位稀土元素分布模式基本一致, 轻重稀土元素之间有明显的分馏。 该方法表明: 各元素的线性关系良好, 相关系数≥0.999 7; 相对标准偏差(RSD)<5.0%, 相对误差<10.0%; 除了Sc的检出限稍高, 其他元素的检出限均能达到ng·L-1。 因此, 该方法适用于沉积物中稀土元素的定量分析。
普里兹湾 电感耦合等离子体质谱 沉积物 稀土元素 Prydz Bay Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry Sediment Rare earth element 光谱学与光谱分析
2012, 32(7): 1950
1 菏泽学院 物理系, 山东 菏泽 274015
2 中国科学院 近代物理研究所, 甘肃 兰州 730000
用湿氧化法在单晶硅表面生长了非晶态SiO2薄膜,再用高能Pb和Xe离子对薄膜进行辐照,最后用荧光光谱分析了辐照参数(剂量、电子能损值)与发光特性改变的相关性。研究发现,快重离子辐照能显著影响薄膜的发光特性,进一步分析显示,辐照导致了SiO2薄膜内O—Si—O缺陷、缺氧缺陷和非桥式氧空位缺陷的产生,且缺氧缺陷和非桥式氧空位缺陷的数量会随Pb离子辐照剂量的增加而增多,而O—Si—O缺陷和缺氧缺陷的形成需要较高的电子能损值。
光致发光谱 重离子辐照 缺陷 photoluminescence swift heavy ion irradiation defect





